
Inverse Functions Iitutor
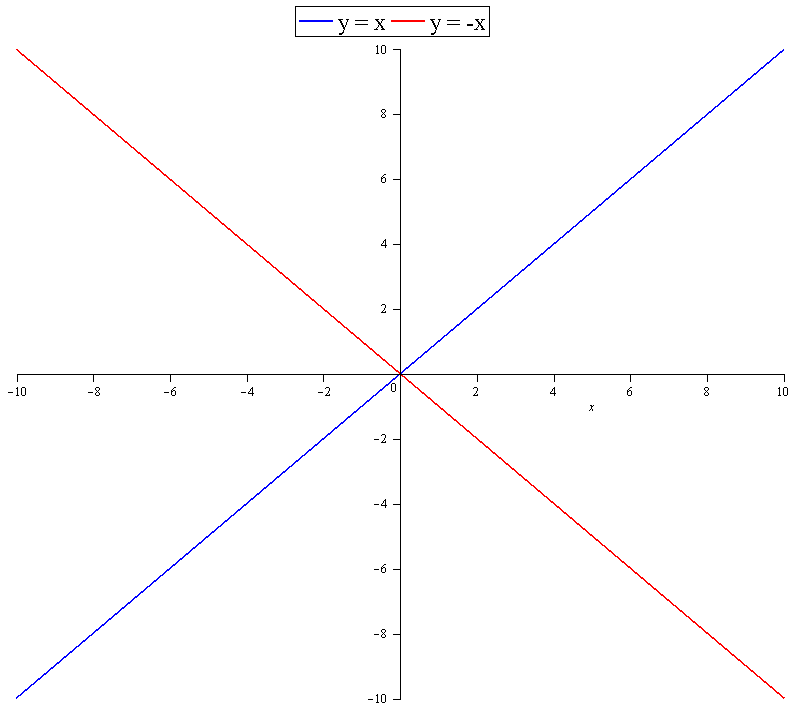
An inverse function is a reflection over the * (1 Point) None of these answers The line y = x У ахis X axis 4 Please look at the handout to see this question Marco created a table for the function, f(x) Which table correctly shows the table for the inver function?One can find the inverse of any object geometrically by reflecting it over the line y=x Performing such a reflection on x=y² gives the function f(x) = x² So just as a function's reflection over y=x may not be a function (reflect sin(x) over y=x for example), so too a relation reflected over y=x may result in an object that is a function
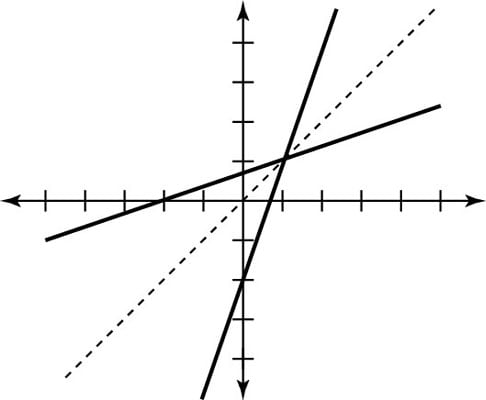
Inverse function reflection over y=x
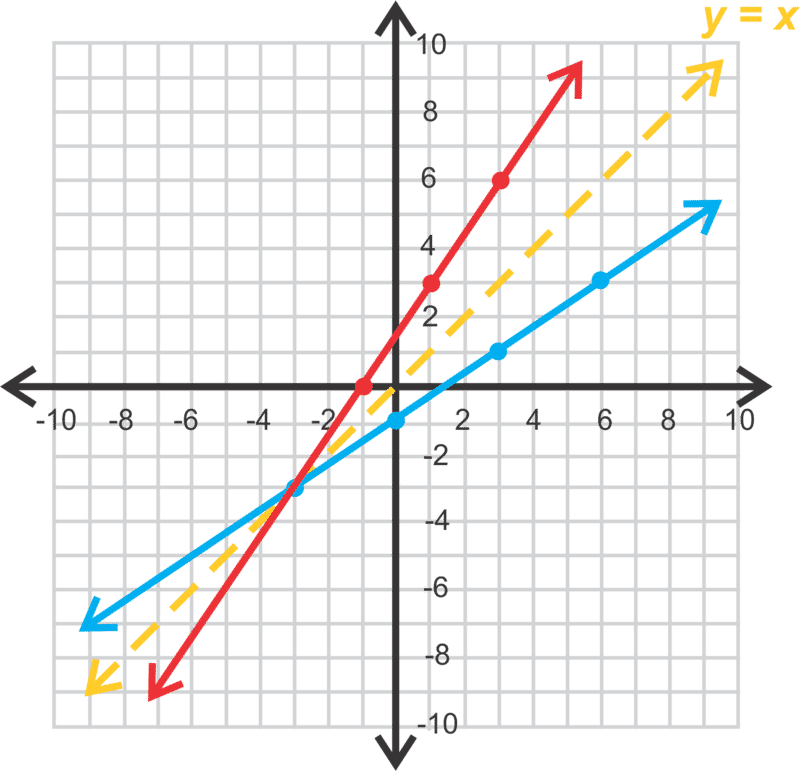
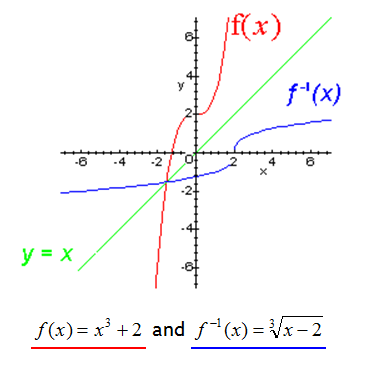
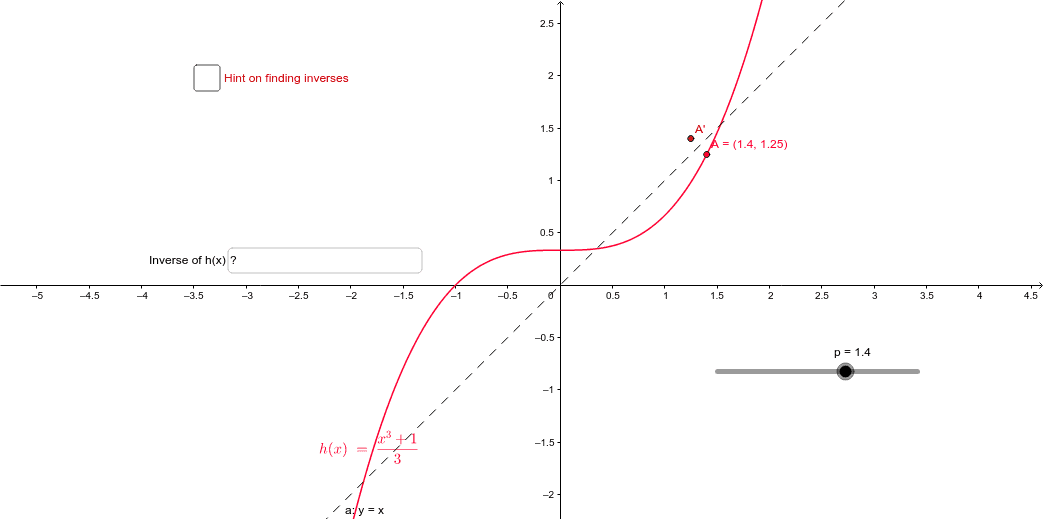
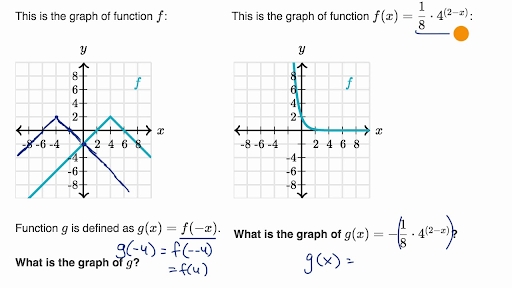
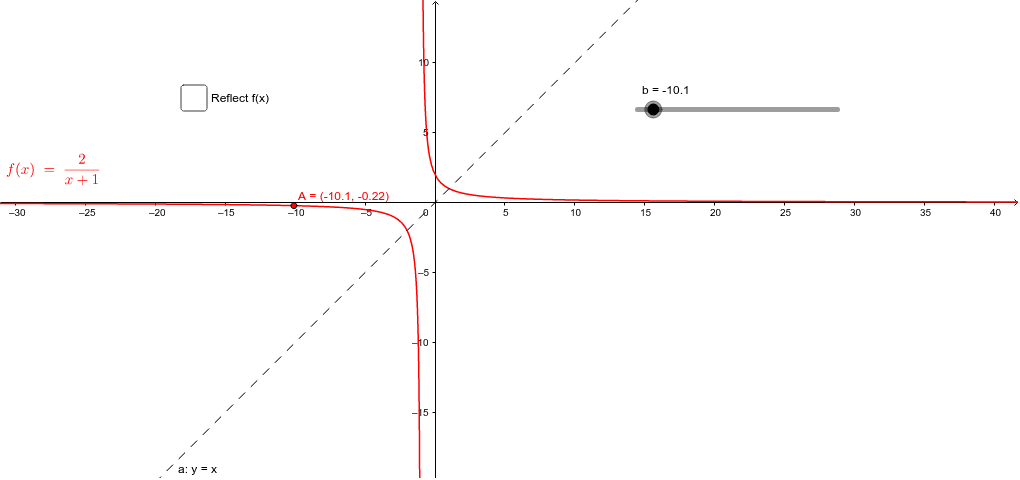
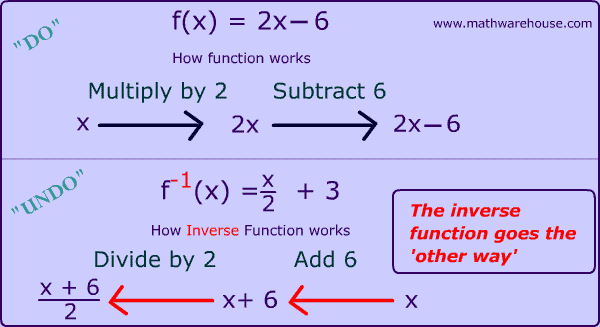
Inverse function reflection over y=x-This works because the graph of the inverse of a function is the reflection of the graph of the function over the line y=x So ` ` `f(x)=7x^34 ==> y=7x^34 ` Exchanging x and y we getHow to find the inverse of a function Switch x and y, and then solve for y Ex f(x) = 5x x = 5y y = x/5 An Inverse is just a reflection of a function The two functions will be symmetric over the line y = x To determine if the inverse of a function is a function, graph the function, and apply the horizontal line test If any horizontal line intersects the function more than once the inverse
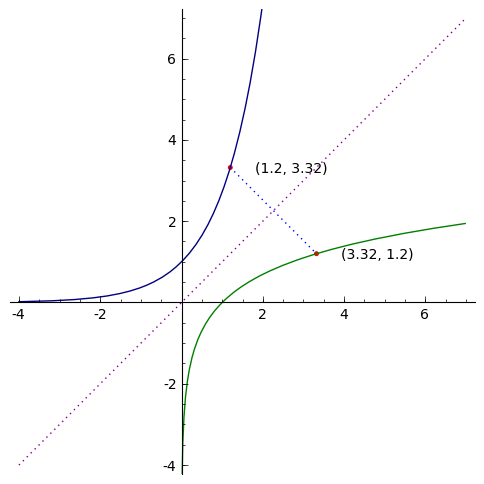
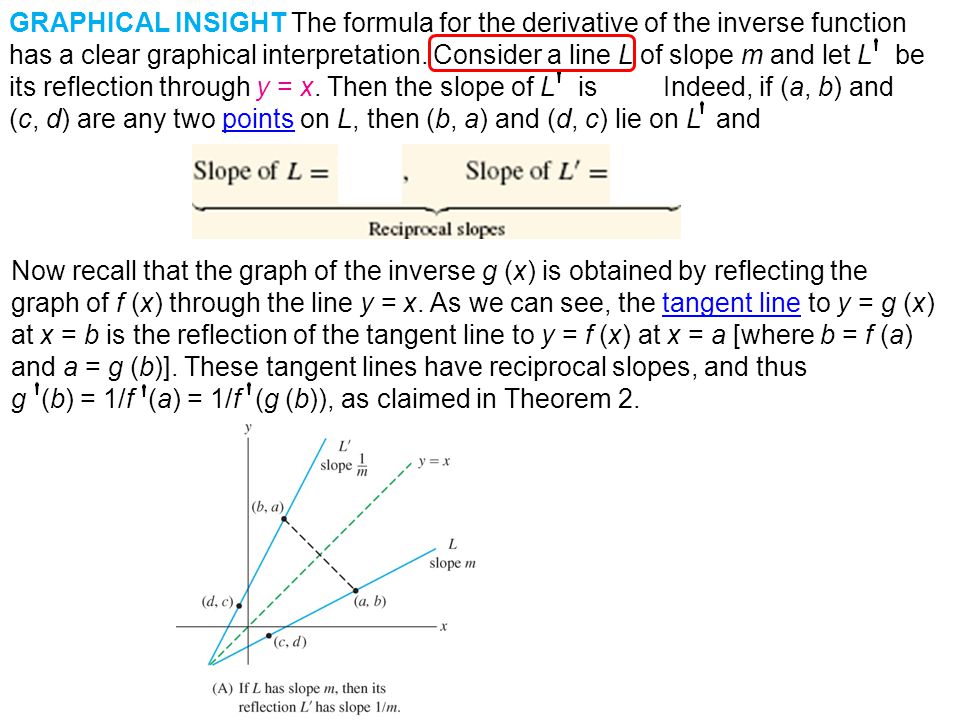
Derivatives Of Inverse Functions
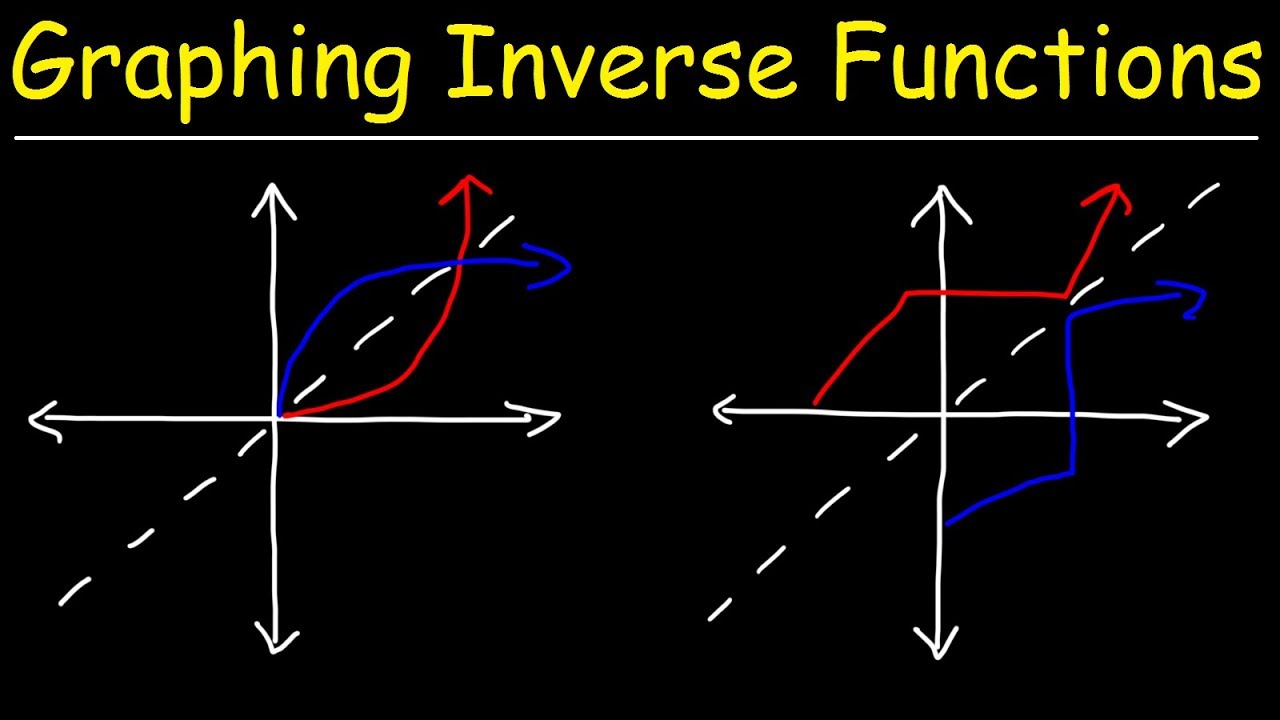
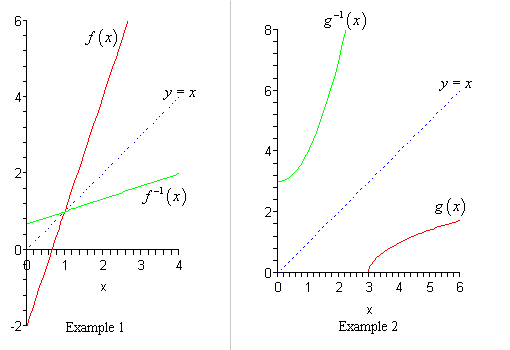
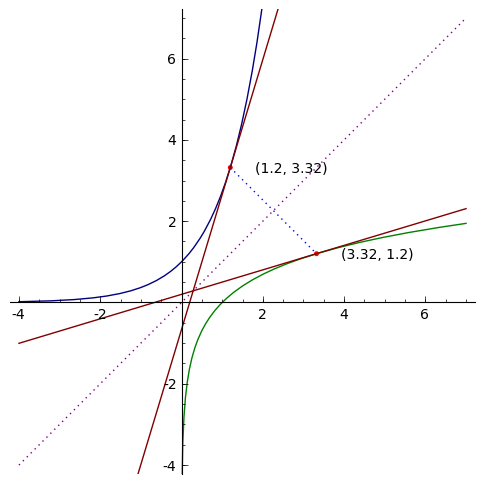
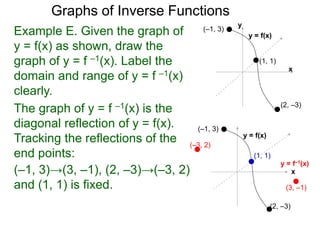
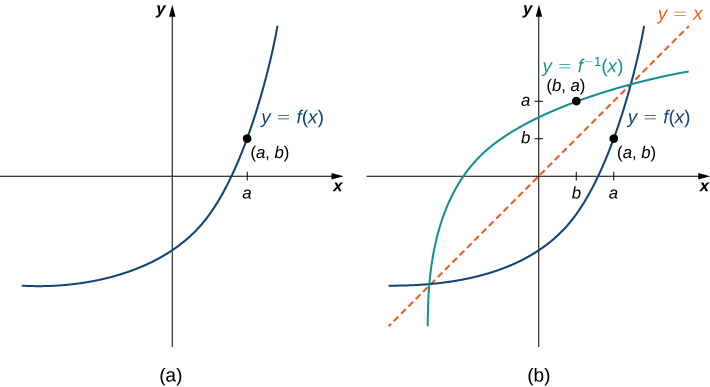
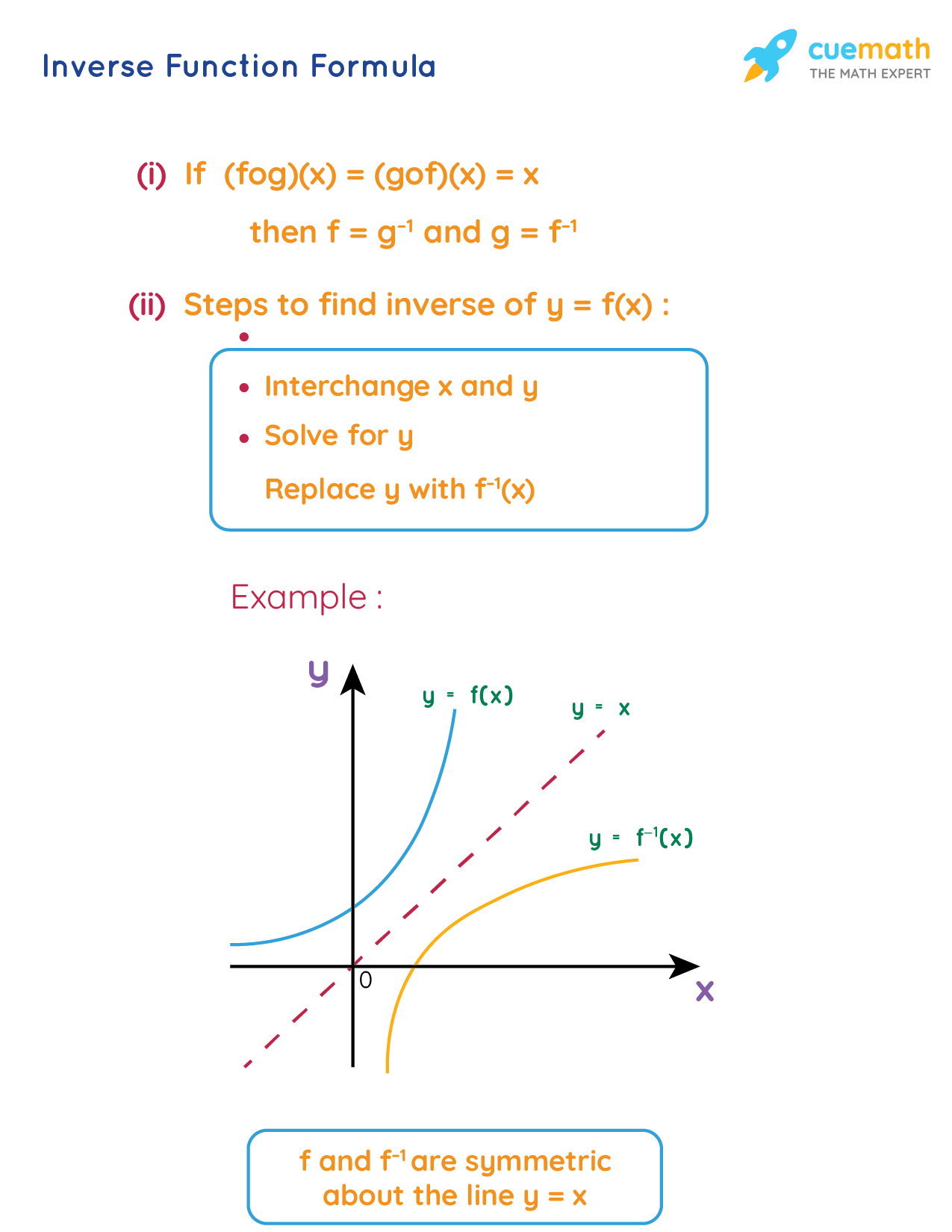
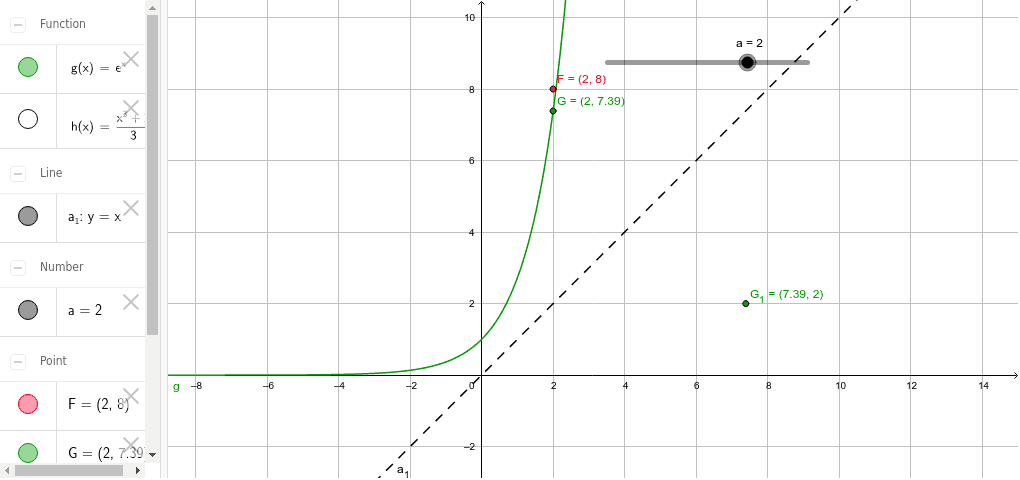
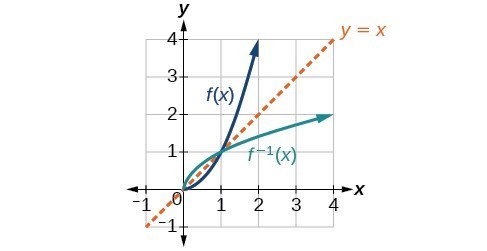
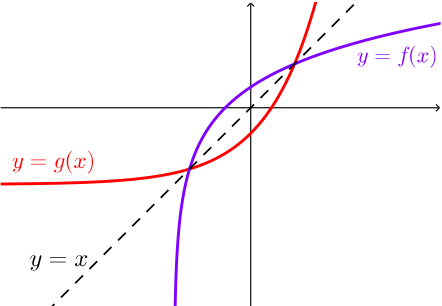
To graph the inverse of the sine function, remember the graph is a reflection over the line y = x of the sine function Notice that the domain is now the range and the range is now the domain Because the domain is restricted all positive values will yield a 1 st quadrant angle and all negative values will yield a 4 th quadrant angleIf you notice, the inverse function (red) is a reflection of the original function (blue) across the line y = x This is true for all functions and their inverses You can also check that you have the correct inverse function beecause all functions f(x) and their inverses f 1 (x) will follow both of the following rules (f ∘When reflecting coordinate points of the preimage over the line, the following notation can be used to determine the coordinate points of the image r y=x =(y,x) For example For triangle ABC with coordinate points A(3,3), B(2,1), and C(6,2), apply a reflection over the line y=x By following the notation, we would swap the xvalue and the y
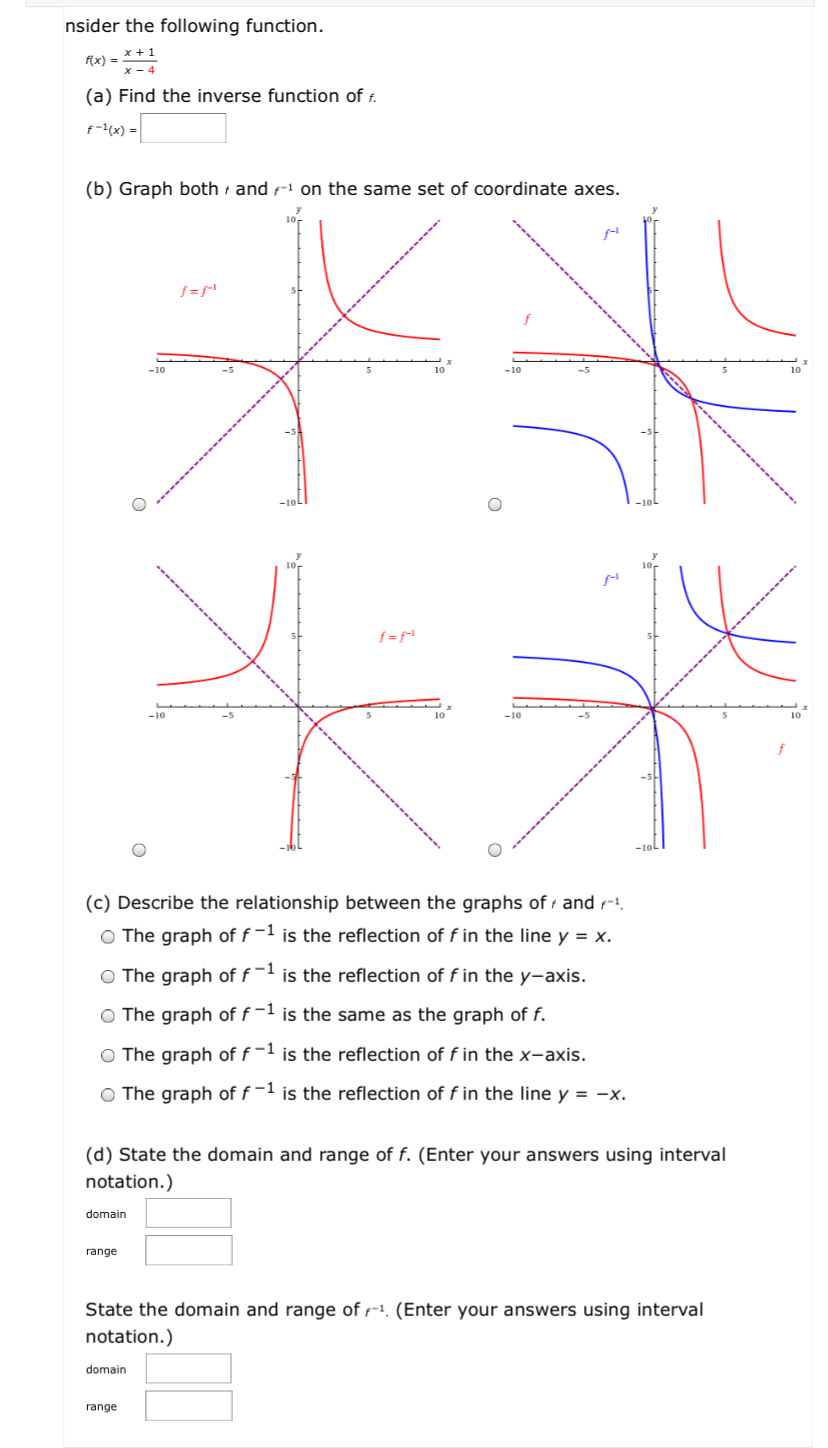
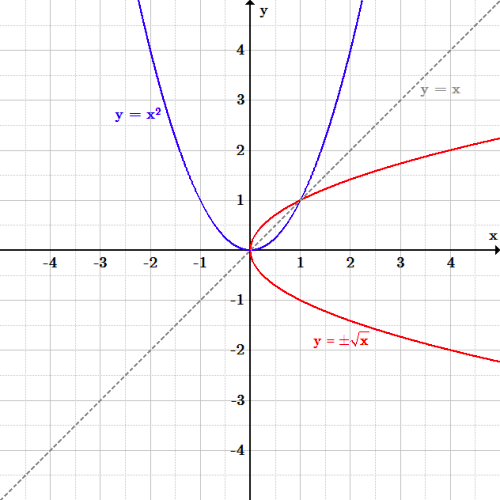
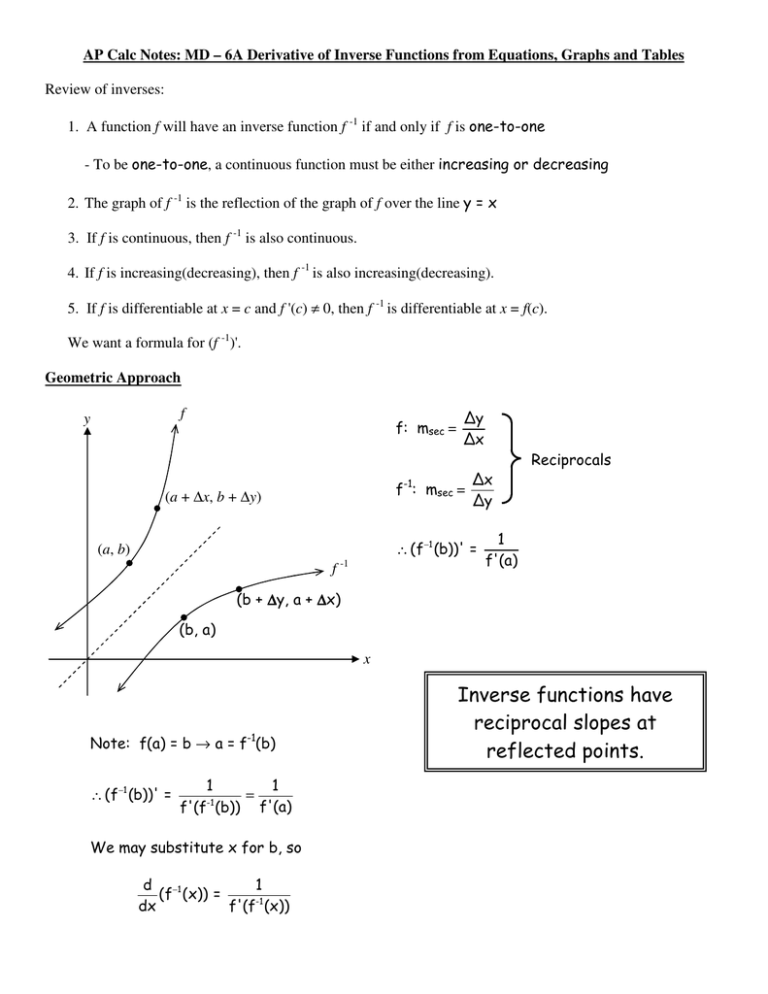
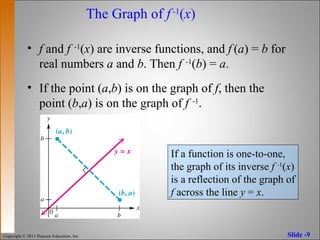
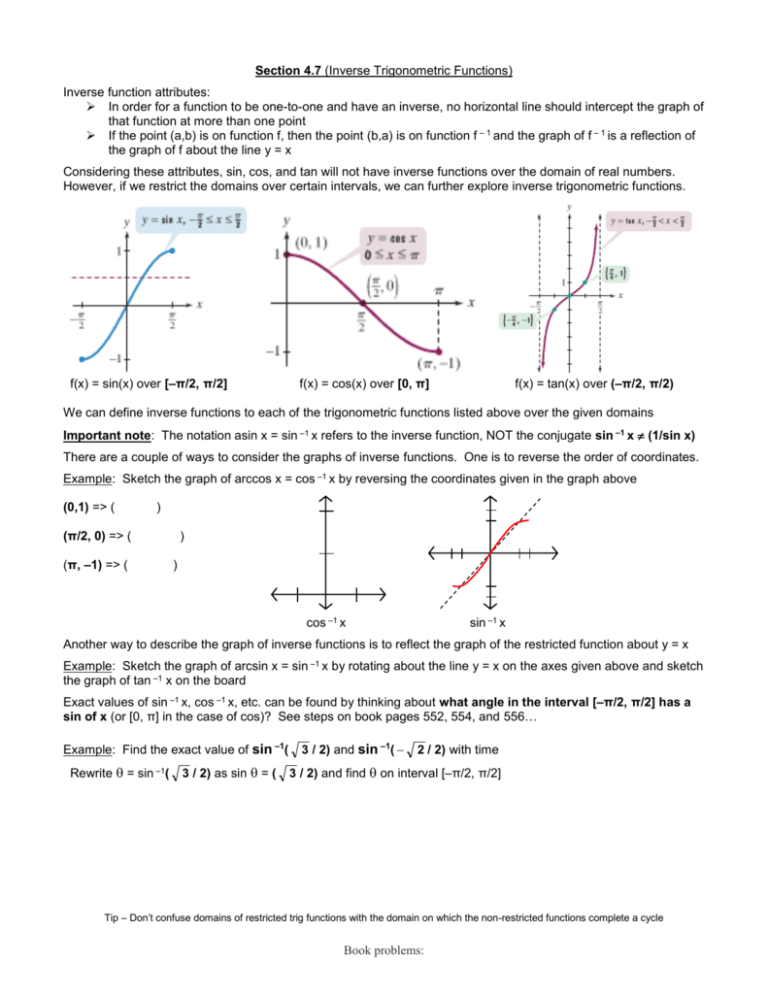
The elaborate way of describing the situation is consider a function f X → Y, X being the domain of the function, and Y being the target space There is a left inverse g Y → X satisfying g ( f ( x)) = x for all x ∈ X, if and only if the original f was onetooneIf f has an inverse, then its graph will be the reflection of the graph of f over the line y = x The graph of f and its reflection over y = x are drawn below *Note The reflected graph does not pass the vertical line test, so it is not the graph of a function Therefore, the function y = x 2 does not have an inverse function The reflection of the graph is an inverse relation, but it is not STEP ONE Rewrite f (x)= as y= If the function that you want to find the inverse of is not already expressed in y= form, simply replace f (x)= with y= as follows (since f (x) and y both mean the same thing the output of the function) STEP ONE Swap X and Y
Inverse function reflection over y=xのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Inverse function reflection over y=x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「Inverse function reflection over y=x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Inverse function reflection over y=x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | 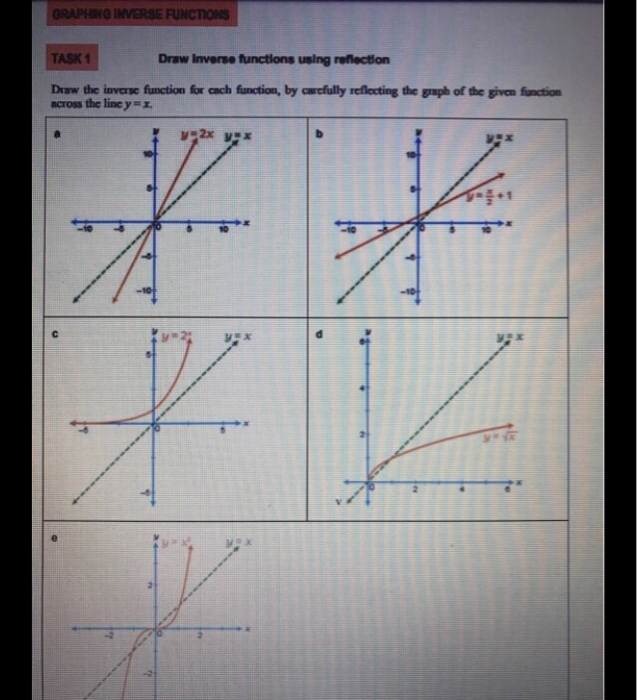 | 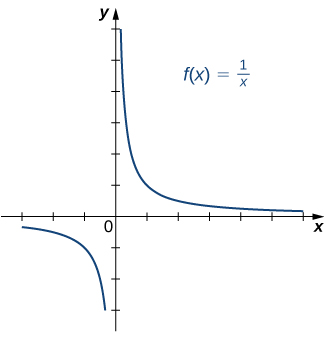 |
 | 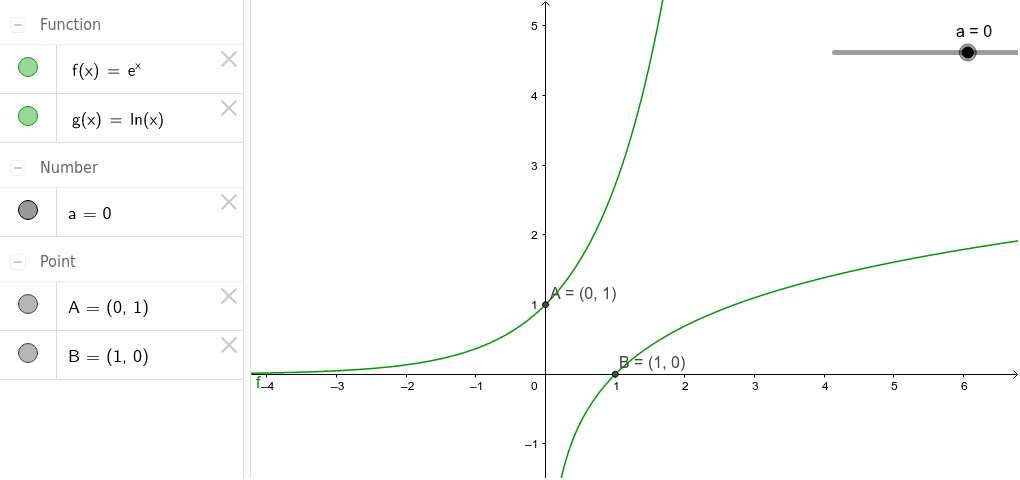 | |
 | 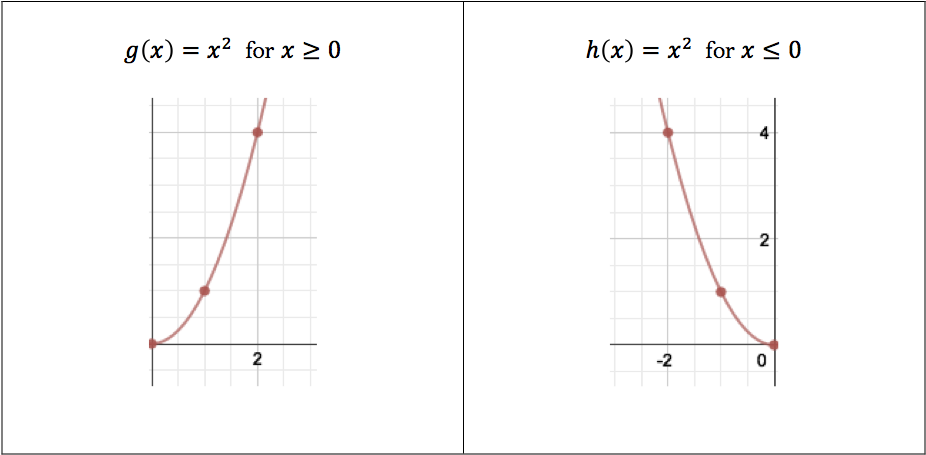 |  |
「Inverse function reflection over y=x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 | 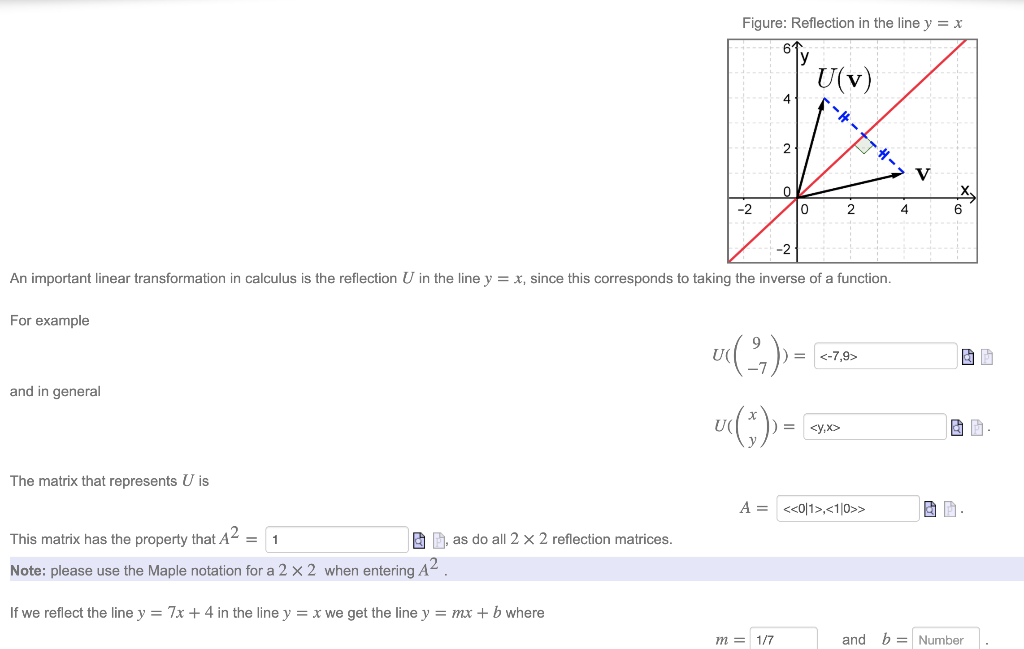 | |
 | ||
「Inverse function reflection over y=x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「Inverse function reflection over y=x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Inverse function reflection over y=x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
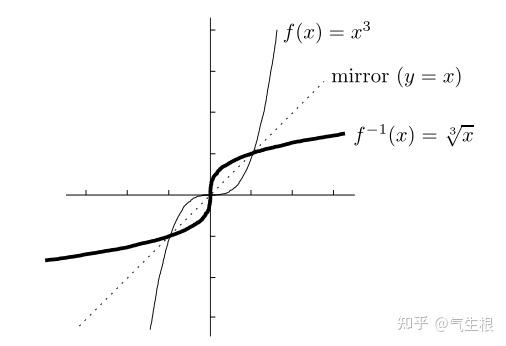 |  | |
 | 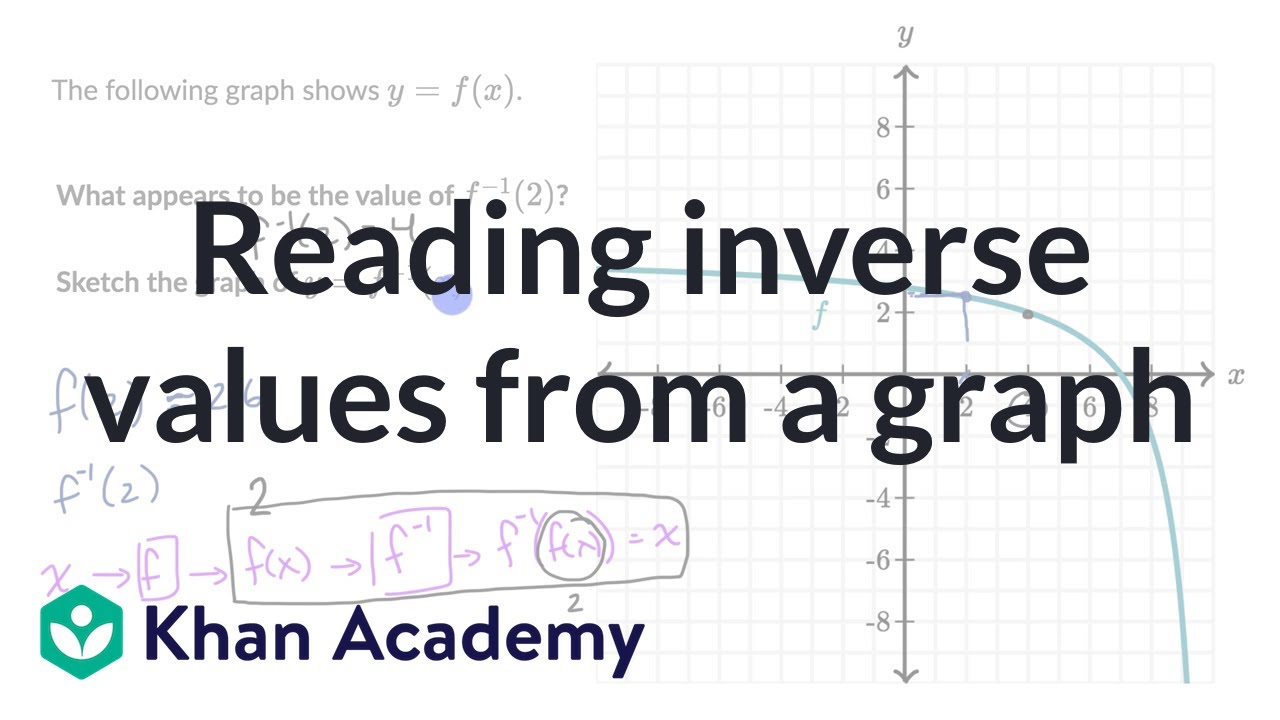 |  |
 |  | |
「Inverse function reflection over y=x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
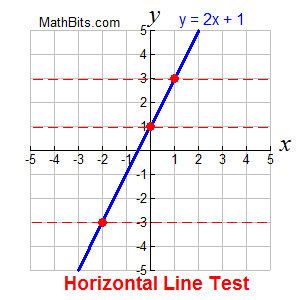 |  | |
 |  | |
「Inverse function reflection over y=x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
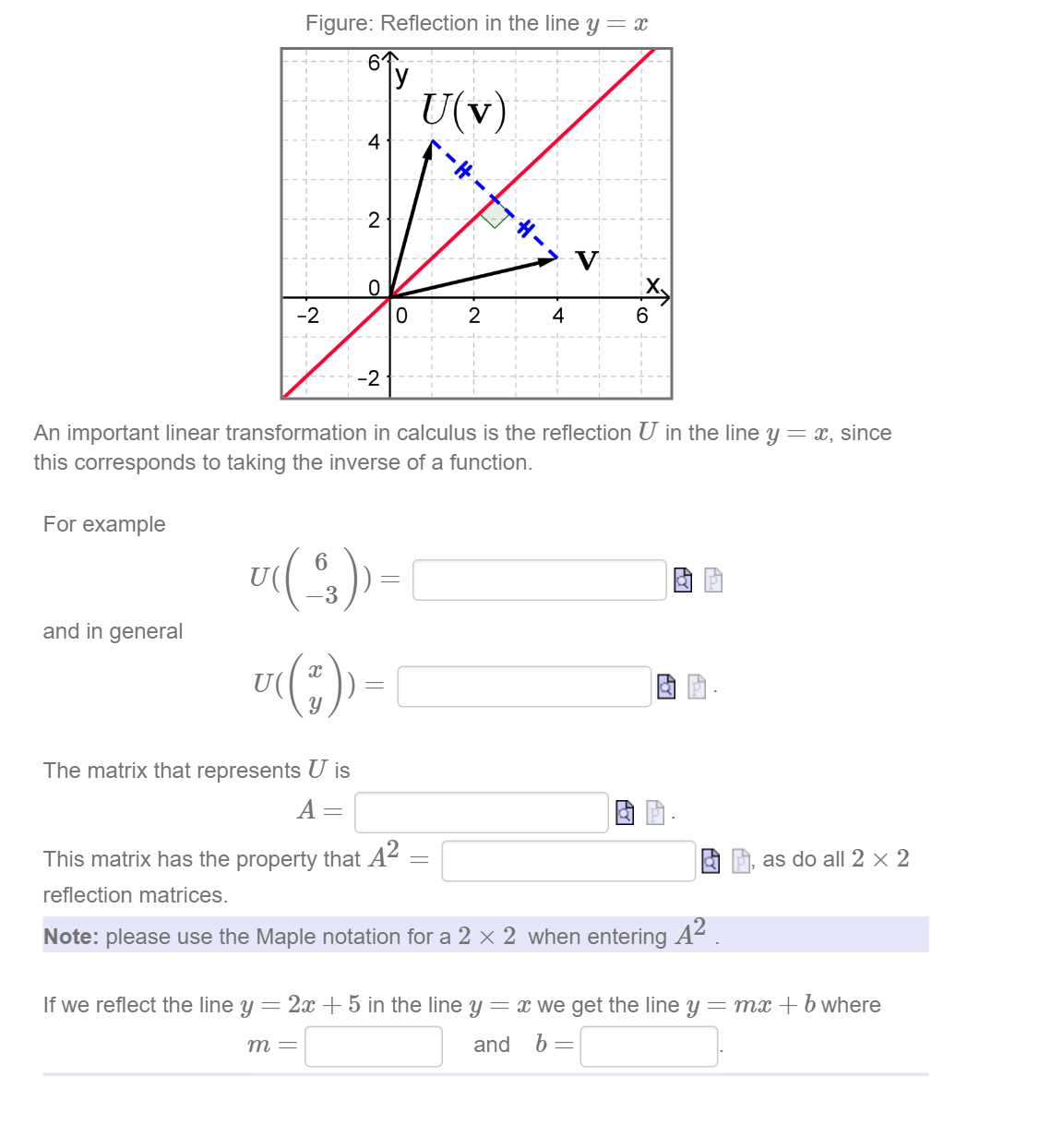 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「Inverse function reflection over y=x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 | ||
 |  | |
「Inverse function reflection over y=x」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
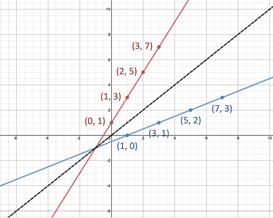
Points on the identity function (y=x) will remain on the identity function when switchedF 1)(x) = x
Incoming Term: inverse function reflection over y=x,



